Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction
Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction (PTTD) is a condition caused by changes in the tendon, impairing its ability to support the arch. This results in flattening of the foot. Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is often called adult acquired flatfoot because it is the most common type of flatfoot developed during adulthood.
Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is a condition caused by changes in the tendon, impairing its ability to support the arch. This results in flattening of the foot. PTTD is often called adult acquired flatfoot because it is the most common type of flatfoot developed during adulthood.
The posterior tibial tendon serves as one of the major supporting structures of the foot, helping it to function while walking. PTTD is a condition caused by changes in the tendon, impairing its ability to support the arch. This results in flattening of the foot.
Although this condition typically occurs in only one foot, some people may develop it in both feet. PTTD is usually progressive, which means it will keep getting worse, especially if it is not treated early.
Causes
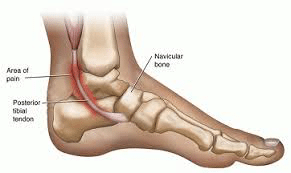
Overuse of the posterior tibial tendon is often the cause of PTTD. In fact, the symptoms usually occur after activities that involve the tendon, such as running, walking, hiking or climbing stairs.
Symptoms
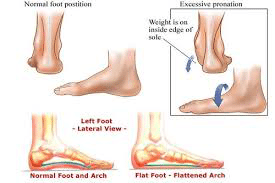
The symptoms of PTTD may include pain, swelling, a flattening of the arch and an inward rolling of the ankle. As the condition progresses, the symptoms will change.
For example, when PTTD initially develops, there is pain on the inside of the foot and ankle (along the course of the tendon). In addition, the area may be red, warm and swollen.
Later, as the arch begins to flatten, there may still be pain on the inside of the foot and ankle. But at this point, the foot and toes begin to turn outward and the ankle rolls inward.
As PTTD becomes more advanced, the arch flattens even more and the pain often shifts to the outside of the foot, below the ankle. The tendon has deteriorated considerably, and arthritis often develops in the foot. In more severe cases, arthritis may also develop in the ankle.
Diagnostic Procedures
Besides the clinical diagnosis, radiographic evaluation can be used to asses deformity and the possible presence of degenerative arthritis or other causes of pes planus. MRI has the highest sensitivity, specificity and accuracy, but ultrasound is less expensive and almost as sensitive and specific as MRI.
Treatment
Treatment options per stages of PTTD are determined on the basis of whether there is an acute inflammation and whether the foot deformity is fixed or flexible. They involve the following.
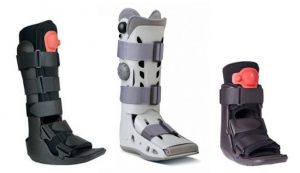
Immobilization: via a short-leg cast or CAM walker boot or Triloc Ankle Brace allows the inflammation to reduce and tendon to heal.
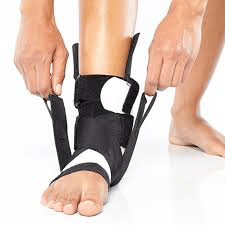
The Richie Brace® is a revolutionary alternative to traditional ankle braces and ankle-foot orthoses (AFO’s). The lightweight construction and low profile design features of the Richie Brace allows better shoe fit, more freedom of movement and reduced pain from injury. TFAAC Podiatrists are highly trained and specialise in prescribing these revolutionary customs made braces. The Richie Brace has become a gold standard treatment in the orthotics industry. It is universally recognized by Podiatrists, Pedorthists, Orthotists and Orthopedic surgeons as a unique, breakthrough technology to treat a wide variety of foot and ankle pathologies such as foot drop, ankle arthritis, ankle sprains and many other ankle injuries.
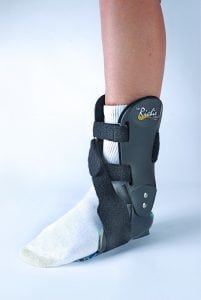
Physical Therapy: balancing and strengthening exercises help rehabilitate the tendon and muscle including static stretching of gastrocnemius and soleus muscle, concentric/eccentric training of the posterior tibialis.

Medications: nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen, help reduce the pain and inflammation.
Shoe modifications: Your Podiatrist may recommend particular types of footwear and recommend modifications to your shoes to aid mobility and alleviate symptoms.
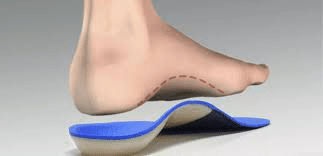
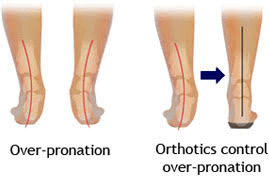
Orthotic Therapy: Optimisation of foot loading management by means of foot orthoses and adequate footwear is the most important and effective means of therapy. The primary function of the orthotic is to provide arch support and correct the flexible component of the deformity.
At the Foot and Ankle Clinic our highly qualified team of Podiatrists are all members of the Australian Podiatry Association and offer a combined 50 years’ experience. They are trained to diagnose and effectively treat Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction via a range of effective treatments.
Put your feet in our hands! See us today in Chadstone, Moe, Sale, Traralgon, Warragul & Online Store and Retail Enquiries. NO REFERRAL NEEDED!.


