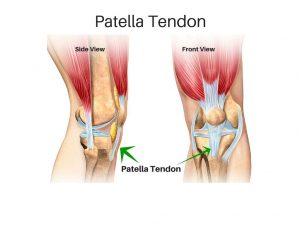
Patella Tendonitis (“Jumper’s Knee”)
Patellar tendinopathy (or as it is commonly known patellar tendonitis or tendinitis) is an overuse injury affecting your knee. It is the result of your patella tendon being overstressed.
A common name for it is Jumper’s Knee.
The greatest level of stress through the patella tendon is during jumping and landing activities. During jumping, the quadriceps muscles provide an explosive contraction, which straightens the knee and pushes you into the air. When landing, the quadriceps muscle helps to absorb the landing forces by allowing a small amount of controlled knee bend.
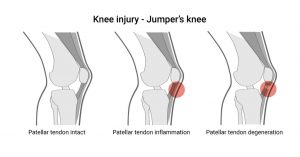
Excessive jumping or landing strains the patella tendon. At first the damage may only be minor and not cause any problem. However, if the tendon is repeatedly strained, the lesions occurring in the tendon can exceed the rate of repair. The damage will progressively become worse, causing pain and dysfunction.
The result is a patellar tendinopathy (tendon injury).
Causes of Patella Tendonitis
Patellar tendinitis is a common overuse injury, caused by repeated stress on your patellar tendon. The stress results in tiny tears in the tendon, which your body attempts to repair. But as the tears in the tendon multiply, they cause pain from inflammation and weakening of the tendon. When this tendon damage persists for more than a few weeks, it’s called tendinopathy.
Symptoms of Patella Tendonitis
Pain is the first symptom of patellar tendinitis, usually between your kneecap and where the tendon attaches to your tibia (shinbone).
The pain in your knee may:
- At first be present only as you begin physical activity or just after an intense workout
- Worsen until it interferes with playing your sport
- Eventually interfere with daily movements such as climbing stairs or rising from a chair
Diagnosis of Patella Tendonitis
During the exam, your Podiatrist may apply pressure to parts of your knee to determine where you hurt. Usually, pain from patellar tendinitis is on the front part of your knee, just below your kneecap.
Imaging tests
Your Podiatrist may request one or more of the following imaging tests:
- X-rays. X-rays help to exclude other bone problems that can cause knee pain.
- Ultrasound. This test uses sound waves to create an image of your knee, revealing tears in your patellar tendon.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). MRI uses a magnetic field and radio waves to create detailed images that can reveal subtle changes in the patellar tendon.
Treatment for Patella Tendonitis
Treatment typically depends on the severity and duration of your injury.
Conservative measures to reduce pain, rest your leg, and stretch and strengthen your leg muscles are generally the first line of treatment. Your doctor will usually advise a period of controlled rest, where you avoid activity that puts force on the knee.
Medication
Your Podiatrist may prescribe over-the-counter non-steroidal anti-inflammatories for short-term pain and inflammation reduction.
Physical Therapy and Exercises:
The goal of physical therapy is to reduce your pain and inflammation and to stretch and strengthen your leg and thigh muscles.
Your Podiatrist will develop an exercise program for you that may include the following:
- Stretches.
- Isometric exercises.
- Eccentric exercises.
- Flexibility exercises for the thigh and calf.
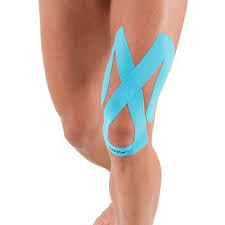
Taping / Strapping
Patella taping to encourage correct tracking of the kneecap is often done and can instantly reduce pain by preventing the kneecap constantly rubbing on the sore spot. One patella taping technique is done to control the position of the patella and is often applied for performing CMP exercises. The second general patella taping technique is ideal for returning to sport as it encourages correct patella tracking but is not restrictive. A patella knee support can help support the patella and relieve pain.
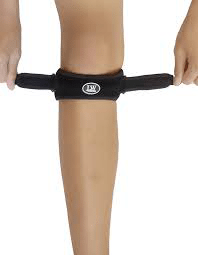
Knee Braces and Splints
There is an extensive range and variety of knee braces and splints designed to stabilise and enhance knee alignment and patella femoral tendon tracking.
Biomechanical Assessment, Gait Evaluation & Custom Orthotic Therapy
Poor foot and ankle function and alignment can cause abnormal rotational forces that contribute to the development of Patella Tendonitis. Your Podiatrist should perform a thorough assessment of your gait and alignment and if abnormality exists recommend or prescribe appropriate orthotic therapy to address this.
Injection Therapy
Treatments such as ultrasound guided injection therapy and dry needling have been found to relieve pain and help healing.
Shockwave Therapy
Extracorporeal shockwave therapy has shown to reduce pain for up to two years.
Surgery
When other treatments aren’t successful in relieving pain, your Podiatrist may recommend surgery to repair the patellar tendon.
At the Foot and Ankle Clinic our highly qualified team of Podiatrists are all members of the Australian Podiatry Association and offer a combined 50 years’ experience. They are trained to diagnose and effectively treat Patellar Tendinopathy via a range of proven treatments.
Put your feet in our hands! See us today in Chadstone, Moe, Sale, Traralgon, Warragul & Online Store and Retail Enquiries. NO REFERRAL NEEDED!.


